Managing Products
Introduction
This guide describes how to query and manage products from the Nautical GraphQL API.
Retrieving a list of products
To fetch a product list, you need to run the products query. The products list is a paginated collection.
You can either retrieve a single product or a list of products. You may require a list of products in many situations, for example, when you need to simply display the catalog in your storefront, or to provide a third party service with a list of products available in your store.
Let's take a look at an example query to fetch a list of products:
{
products(first: 5) {
edges {
node {
id
name
}
}
}
}
In this example, we requested the following fields for each product:
id: the unique product ID, most operations will require one.name: the name of the product. The response returns these fields for two products, because of thefirst: 2argument in the query:
{
"data": {
"products": {
"edges": [
{
"node": {
"id": "UHJvZHVjdYo0NTU=",
"name": "Orange Juice"
}
},
{
"node": {
"id": "UHJvZHVjdDo2TzQ=",
"name": "Apple Juice"
}
}
]
}
}
}
Filtering the list of products
You can filter the results returned by the products query using the optional filter argument. The filter argument accepts filter options from the ProductFilterInput.
Some of the filters that are available include:
productTypes: ID— filter by a given product template.sellers: ID— filter by a given seller.attributes: AttributeInput— filter products with a given attribute.features: FeatureFilterInput— filter products with a given feature.price: ...— filter by base price:price: {lte: Float}— price lower than or equal to given value.price: {gte: Float}— price greater than or equal to given value.
minimalPrice: ...— filter by minimal variant price:minimalPrice: {lte: Float}— price lower than or equal to given value.minimalPrice: {gte: Float}— price greater than or equal to given value.
Searching products
There are two search filters available when querying products:
advancedSearch: Targets specific field(s) for faster performance and tailored results.search: Searches across all fields for broad search results with slower performance.
Advanced search
You can use the advancedSearch parameter with the filter argument for advanced filtering by search term when querying products.
The advancedSearch filter accepts two input fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
searchTerm (required) | A string to search with. |
searchFields | A comma separated list of fields to search across. If no search fields are defined, the filter defaults to searching only by NAME. The fields you can target for search are defined in the ProductSearchFieldEnum. |
Here is an example query that returns the first five products with the term "shiny" in the product name, variant name, description, or category name:
query {
products(
first: 5
filter: {
advancedSearch: {
searchTerm: "shiny"
searchFields: [NAME, VARIANT_NAME, DESCRIPTION, CATEGORY_NAME]
}
}
) {
edges {
node {
id
name
description
}
}
}
}
Basic search
You can use the basic search filter for a broad-match search results when querying products. The search filter accepts a string input that will be used to search across all product fields.
If you experience performance issues with the basic search filter, try using advancedSearch instead.
Here is an example query that looks for the first five products that mention the term "juice":
{
products(
first: 5
filter: {
search: "juice"
}
)
{
edges {
node {
id
name
description
}
}
}
}
Sorting the list of products
In products you can also sort the results using two sortBy arguments: field and direction.
field: the field to use for sorting the results from several predefined choices:DATE: sort products by last update.MINIMAL_PRICE: sort products by minimal variant price.NAME: sort products by name.PRICE: sort products by base price.PUBLICATION_DATE: sort products by publication date.PUBLISHED: sort products by publication status.TYPE: sort products by product template.
direction: The direction for sorting items:ASC: sort ascending.DESC: sort descending.
For all of the available fields to sort by, see the ProductOrder API reference.
This example shows how to sort the products list by the minimal variant price, lowest to highest:
{
products(
first: 2
sortBy: { field: MINIMAL_PRICE, direction: ASC }
) {
edges {
node {
name
minimalVariantPrice {
amount
currency
}
}
}
}
}
Viewing product availability
The isAvailable field on the product object contains the availability status of products.
The product isAvailable field is a boolean that is either true or false, based on the following logic calculation:
| If | Then |
|---|---|
| The product is not published or the publication date is in the future | false |
| The product is not available for purchase or the available for purchase date is in the future | false |
| The stock is not available for the country where the request is made | false |
None of the above false conditions are met and at least one inventory quantity is available in the country where the request is made, based on the warehouse shipping zones | true |
The stock availability by country is determined based on warehouse shipping zones and the requestor's IP address, which infers the country
For example, if the product Apple Juice is missing a warehouse and a shipping zone for the country where the request is made, the isAvailable field will be false.
However, once a warehouse and the Americas shipping zone are assigned to the product, the isAvailable will change to true.
Retrieving a single product
To get details about a single product, use the product query, which requires only one input field:
id: the unique product ID.
Here is the example query that fetches a single product:
query {
product(id: "UHJvZHVjdDoxMTU=") {
id
name
}
}
For more details about this query, see the product query API reference.
Retrieving product variants
To obtain product variants, query the variants field on the Product type:
{
products(first: 1) {
edges {
node {
id
name
variants {
id
name
}
}
}
}
}
Like products, here we're asking for two fields from each variant:
id: the unique variant ID.name: the name of the variant.
The For more details about the fields you can query under the variants field, see the ProductVariant API reference.
Pricing
Use the pricing field of products and variants to obtain pricing information.
Here are the available fields for product pricing:
type ProductPricingInfo {
priceRange: TaxedMoneyRange
priceRangeUndiscounted: TaxedMoneyRange
discount: TaxedMoney
onSale: Boolean
}
And similar fields for product variants:
type VariantPricingInfo {
price: TaxedMoney
priceUndiscounted: TaxedMoney
discount: TaxedMoney
onSale: Boolean
}
The main difference is that products don't have a price point, instead they offer a price range that includes all of their variant prices.
Here are the money types returned by the above:
type TaxedMoneyRange {
# lowest price
start: TaxedMoney
# highest price
stop: TaxedMoney
}
type TaxedMoney {
# before tax
net: Money!
# after tax
gross: Money!
# gross - net
tax: Money!
# repeated for convenience
currency: String!
}
type Money {
amount: Float!
currency: String!
}
Description
There are three fields that store the product description, as explained in the following table:
| Field | Usage |
|---|---|
descriptionHtml | HTML-formatted description. You must enclose all text in valid HTML tagging. For example, all paragraphs must be enclosed in a If you have text outside of a valid HTML tag, users will experience issues with editing that text in the Dashboard text editor. |
descriptionJson | (Deprecated) JSON-formatted description. This is the legacy description field and will not be used going forward. This field will be removed by September 2023. While this field is being deprecated, you can still use it to pass in JSON-formatted descriptions but we strongly suggest you change your workflows to use the new |
description | Plain text description. When you pass a value to descriptionHtml or descriptionJson, the description is converted to plain text and stored in this field. |
The current implementation of descriptionHtml supports the following HTML tags:
- Divider:
<div> - Headings:
<h1>,<h2>,<h3> - Text block:
<p>,<blockquote> - Text decoration:
<strong>,<u>,<i>,<code> - Lists:
<ul>,<ol> - Text align style attribute:
style="text-align: { left | center | justify | right }"
Here's an example query that will return all three description fields:
{
product(id: "UHJvZHVjdDo1MQ==") {
id
name
descriptionHtml
descriptionJson
description
}
}
Images
The Product object contains three fields you can query to return images: thumbnail, images, and imageById.
When you request a specific size for an image for the first time, the API may take longer to respond as it needs to generate a new image that meets the requested size requirements. Subsequent requests for the same size should be faster.
Thumbnail
Use the thumbnail field while querying products to return the main image for the product in a square format.
Here's an example query that will return the thumbnail, optimized for display at 100×100px:
{
products(first: 1) {
edges {
node {
id
name
thumbnail(size: 100) {
url
alt
}
}
}
}
}
Size argument
Optionally, specify the size argument with the thumbnail field to return an image of a specific size in pixels.
The thumbnail image is always a square image. When you request a specific size for the thumbnail image, it will always generate a square image of that size.
Sub-fields
thumbnail supports the following sub-fields:
url: the image's URL.alt: the alternative text to include when displaying the image.
All images
Use the images field while querying products to return all associated product images.
Here's an example query that will return all images, with the largest dimension set to 100px for each:
{
products(first: 1) {
edges {
node {
id
name
images {
url(size: 100)
alt
id
}
}
}
}
}
Sub-fields
images supports the following sub-fields:
url: the image's URL.
Size Argument:- Optionally, specify the
sizeargument with theurlfield to return images in a specific size in pixels.Image sizeWhen you request images of a specific size through the
urlfield, the API generates a new image if the size doesn't match the original image dimensions. The image's largest dimension (width or height) is resized to match the specified size in pixels, while maintaining the original aspect ratio.- For a portrait-oriented image with a height is greater than its width, the new image's width will be equal to the requested size, and its height will be resized to maintain the aspect ratio.
- For a landscape-oriented image with a width is greater than its height, the new image's height will be equal to the requested size, and its width will be resized to maintain the aspect ratio.
- Optionally, specify the
alt: the alternative text to include when displaying the image.id: the ID of the image
Specific image
Use the imageById field while querying a product to return an image matching a specified ID.
Here's an example query that returns a specific image on a given product with the largest dimension set to 100px:
{
product(id: "UHJvZHVjdDo0NTU=") {
id
name
imageById(id: "UHJvZHVjdEltYWdlOjExODg=") {
url(size: 100)
alt
}
}
}
ID argument
The id argument is required to specify the ID of the target image.
Sub-fields
imageById supports the following sub-fields:
url: the image's URL.
Size Argument:- Optionally, specify the
sizeargument with theurlfield to return images in a specific size in pixels.Image sizeWhen you request images of a specific size through the
urlfield, the API generates a new image if the size doesn't match the original image dimensions. The image's largest dimension (width or height) is resized to match the specified size in pixels, while maintaining the original aspect ratio.- For a portrait-oriented image with a height greater than its width, the new image's width will be equal to the requested size, and its height will be resized to maintain the aspect ratio.
- For a landscape-oriented image with a width greater than its height, the new image's height will be equal to the requested size, and its width will be resized to maintain the aspect ratio.
- Optionally, specify the
alt: the alternative text to include when displaying the image.
Example query
Here's a more complex GraphQL query that combines all of the above information:
{
products(first: 2, sortBy: { field: NAME }) {
edges {
node {
id
name
pricing {
priceRange {
start {
gross {
amount
currency
}
}
}
discount {
gross {
amount
currency
}
}
priceRangeUndiscounted {
start {
gross {
amount
currency
}
}
}
}
thumbnail {
url
}
}
}
}
}
Create a product
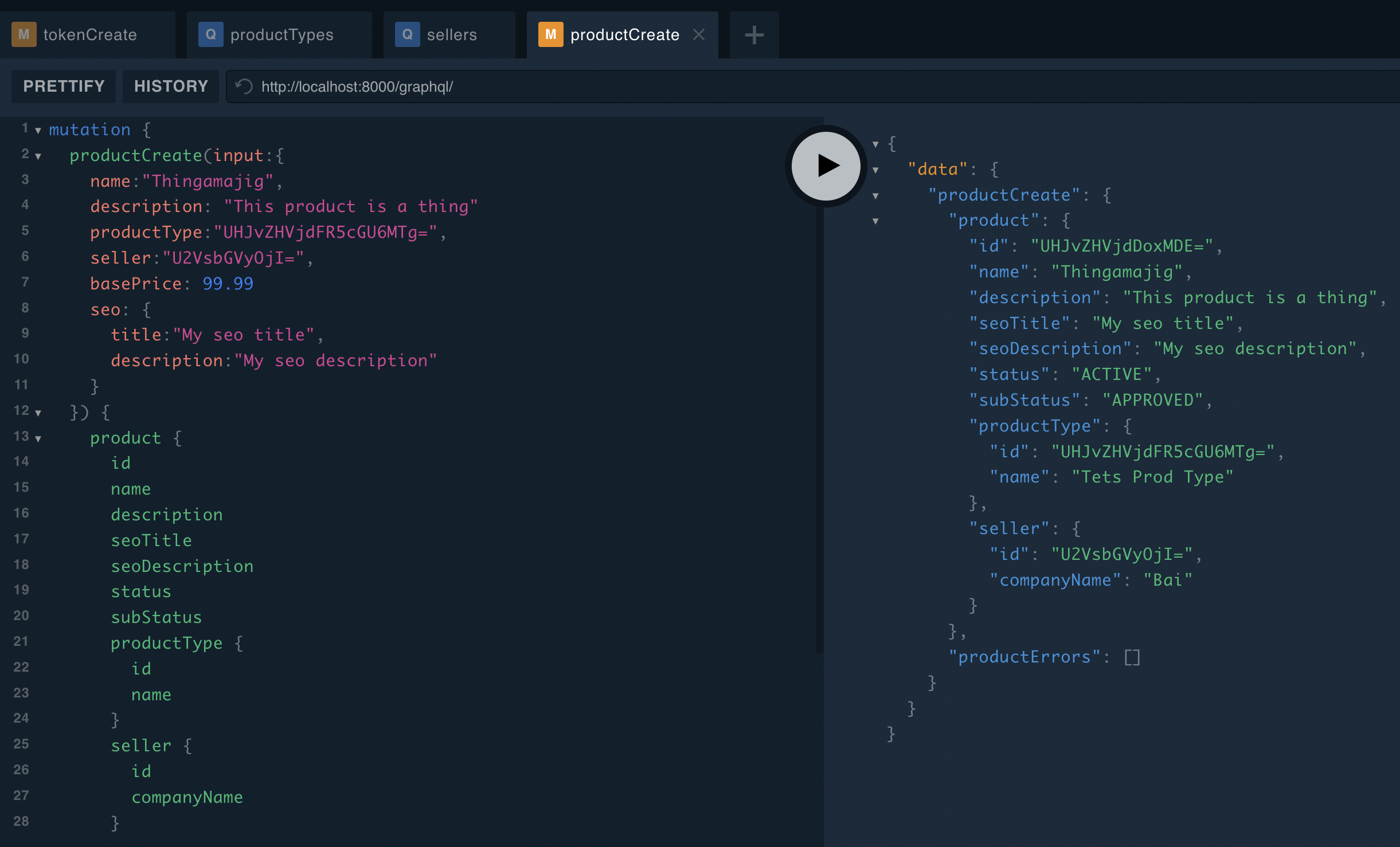
Here is an example of creating a product:
mutation {
productCreate(
input: {
name: "Thingamajig"
description: "This product is a thing"
productType: "UHJvZHVjdFR5cGU6MTg="
seller: "U2VsbGVyOjI="
basePrice: 99.99
seo: { title: "My SEO title", description: "My SEO description" }
}
) {
product {
id
name
description
seoTitle
seoDescription
status
subStatus
productType {
id
name
}
seller {
id
companyName
}
}
productErrors {
field
code
message
}
}
}
In order to assign the product the desired product template and to the desired seller, you'll need the base 64 encoded IDs of each, respectively. You can find these IDs by querying product templates and sellers.
Update a product
In order to update a product, you'll need its ID. In our example, it is "UHJvZHVjdDoxMDE=".
Now let's say we wanted to update the product to make its isPublished field true (it's false by default on product creation). In order to publish the product, it needs to be assigned a product template (which we already did) and it also needs to be assigned a category (which we haven't done yet). In order to assign the product a category, we'll need the category's ID.
Let's use the category ID of "Q2F0ZWdvcnk6MjM=".
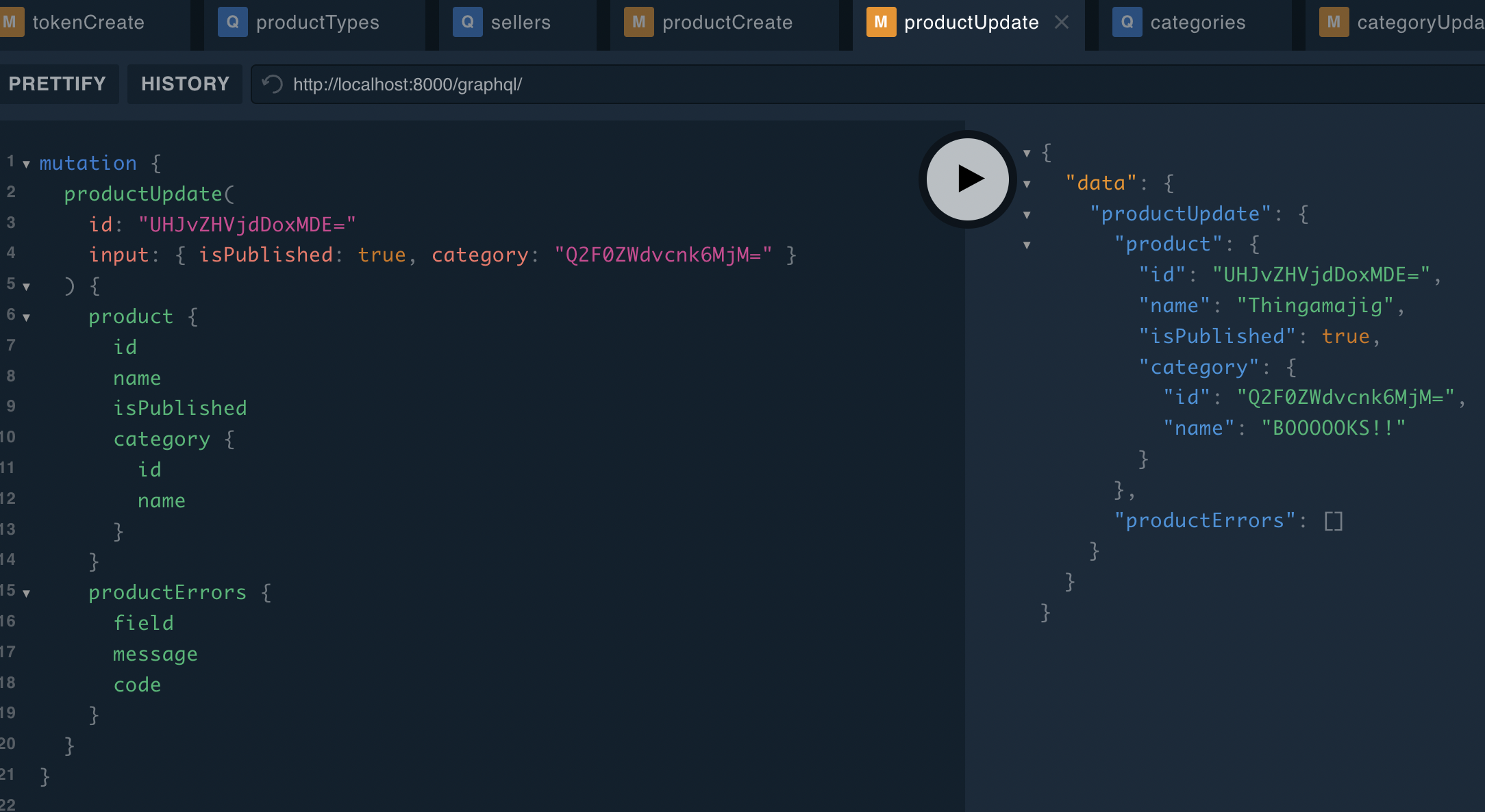
Here is an example of updating a product, in this case updating it with a new category and then publishing it:
{
productUpdate(
id: "UHJvZHVjdDoxMDE="
input: { isPublished: true, category: "Q2F0ZWdvcnk6MjM=" }
) {
product {
id
name
isPublished
category {
id
name
}
}
productErrors {
field
message
code
}
}
}